How to Create a Truly Portable Ubuntu Installation on an External USB HDD or SSD
Update: 17-08-2020 - a few people have asked which NVMe external enclosure I'm using in the photo above. I was using a the 'Plugable Tool-Free NVMe' enclosure, but started to have difficulties with the Realtek RTL9210 controller and/or their USB cables. I was having difficulty removing all partitions from the drive under Ubuntu using GParted - with GParted freezing on device re-scan. I've since switched to the TDBT M.2 NVMe SSD Enclosure (using the JMicron JMS583 controller), which is working great. The enclosure, installation instructions, parts, are all top quality and the heat sink works. The only caveat so far is that a Belkin USB-C cable I have here refused to recognize the TDBT device. The cables that came with the TDBT enclosure work fine. (Note that I'm not in anyway affiliated with TDBT, nor do I have an affiliate link with Amazon.)
Update: 07-02-2021 - C.S.Cameron posted this to askubuntu.com - https://askubuntu.com/questions/1217832/how-to-create-a-full-install-of-ubuntu-20-04-to-usb-device-step-by-step Although I've not tested this yet - it's a great post and appears to support both UEFI and older BIOS/MBR configurations.
Original Post: So this turned out to be fun, and productive - on several levels.
I recently upgraded the SSD in my main desktop computer and found myself with a spare 512GB M.2 NVMe SSD. At first I thought I’d simply use the spare drive for backups or ad hoc storage, but then I recalled that ages ago I’d explored the idea of being able to simply plug the operating system of my choice into the USB port of a computer or laptop, and boot whatever flavor of OS I cared to. At the time, USB 2.0, Firewire or even e-SATA meant that this wasn’t really practical. With USB 3.0 to 3.1 Gen 2 supporting transfer speeds that now range from 5Gbits/s to 10Gbits/s - things are a bit different. Regular SATA-based external SSDs will deliver transfer rates of around 500MB/s, while new M.2 NVMe to SATA bridge enclosures will top out at around 1GB/s (that’s one gigabyte per second, not gigabits). So clearly in terms of storage and bandwidth, there’s nothing here that would interfere with comfortable boot times and data transfer rates for any modern OS.
There’s only fly in the ointment, and that is that during most ‘normal’ operating system (OS) installations - the OS being installed expects to either create, or find just one master boot record (MBR) or just one Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) system partition (ESP). If a UEFI ESP partition already exists, the installing OS will typically give you a choice to overwrite, or modify boot loaders in the ESP with the option of creating a ‘dual boot’ installation. The problem with this process is that the new operating system - whether on an external drive or other, is now ‘bound’ to the computer’s main system partition and boot information. Not only is the external drive dependent on the boot information present in the host computer system partitions, but in most cases the computer won't boot if the external drive is removed. Not what we want.
I did a bunch of reading and found the main Grub docs that describe how to repair/reinstall grub, but more importantly, I found Nicholas Dionysopoulos's post here https://www.dionysopoulos.me/portable-ubuntu-on-usb-hdd/ - which was brilliant and paved the way. Most of what follows is roughly aligned with Nicholas’s post.
Like Nicholas, the machine I’m using to do all of this is a Windows 10 computer, and so if this is the same for you, then section F below will almost certainly apply and your computer will be left with a ‘dual boot’ configuration and Grub menu prompt at boot. If you’re concerned about this, read ahead and review the fixes before proceeding. And as with any OS / disk / partition-level activity, make sure you have backups of everything before you start.
Here are the steps I went through in order to create a truly portable external SSD drive with Ubuntu 19.10 installed. Note that we’re going to create a UEFI bootable portable drive, and so any computer you plug this drive into must be relatively modern with support for UEFI as well as have pretty good hardware support from Ubuntu / Linux.
A. What You’ll Need
To start you’ll need two things:
- A bootable USB thumb drive with the Ubuntu 19.10 installation media. You can create this from a Windows computer using Rufus or from an existing Ubuntu installation with ‘Startup Disk Creator’ - see How to Create a Bootable Linux USB Flash Drive, the Easy Way . Check that you can boot from this thumb drive on the computer you plan on working from. Choose the ‘Try Ubuntu’ option.
- Your target portable external hard drive (HDD, SATA SSD, M.2 NVMe SSD etc.). Note that we’ll re-partition this drive, so backup any data that may already be on the drive as it will be lost during re-partitioning.
B. Getting Started
- Boot your computer using the thumb drive prepared above, and choose ‘Try Ubuntu’.
- Plug in your target portable external hard drive.
- Start GParted. GParted is the partition manager application we’re going to use to prepare the portable hard drive. Once GParted is started - in the upper right corner, change the target drive to your external portable drive. It’s important that you correctly identify this drive as we’re going to re-partition the drive. In the screenshot below - my external and portable drive is identified as /dev/sdb - and it is currently unpartitioned. Unmount (right click and unmount) any currently mounted partitions on this drive and delete all partitions (again - be double sure you’re working on the correct drive).
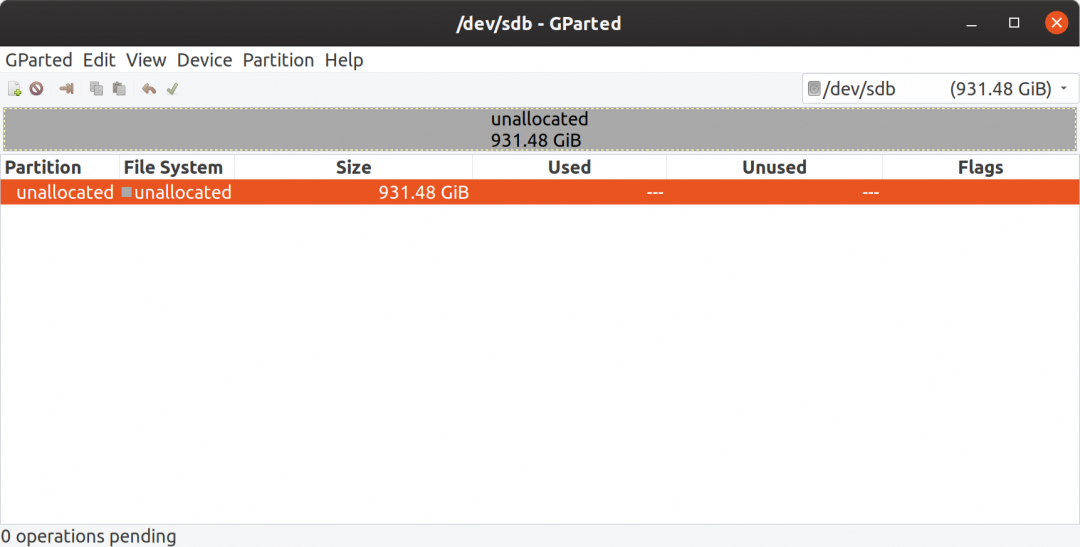
C. Preparing the Portable Drive
We’re going to create three new partitions on the target external drive.
- Again using GParted, right click on the unallocated volume, choose New, and create a 100MB fat32 partition. Click on the green checkmark to apply the pending operation. Once the partition has been created - right click on the newly created partition and select ‘Manage Flags’. Enable the boot and esp flags. When we're done, this partition will become the system ‘boot’ partition, and will include EFI information including the GNU GRUB boot loader. In fact, creating this partition as a working boot volume under EFI using GRUB is the heart of our problem in trying to create a truly portable external OS drive, and so there are a few more steps to complete before we can achieve this.
- Next create an 8GB linux-swap partition. The size of your swap partition may vary and so you’ll need to do a little research to determine the appropriate size for your expected workload. A rule of thumb for modern personal computers with plenty of RAM is to create a swap partition about ½ the size of available RAM if you DO NOT plan on supporting full hibernate (most computers will still suspend or sleep fine).
- Finally, create the main or root / partition for our target portable drive. Create an ext4 partition of whatever size you require for your system. Apply all pending operations and you should now have a disk partition layout that looks similar to the screenshot below. [Note that in my case I still have about 500GB unallocated space as this is a 1TB external drive. Also note that in my ‘real’ setup I created a 64GB ext4 volume for Ubuntu OS, and then when everything was up and running, I created an additional 256GB ext4 volume which I then encrypted with LUKS, and mounted as my /home directory]
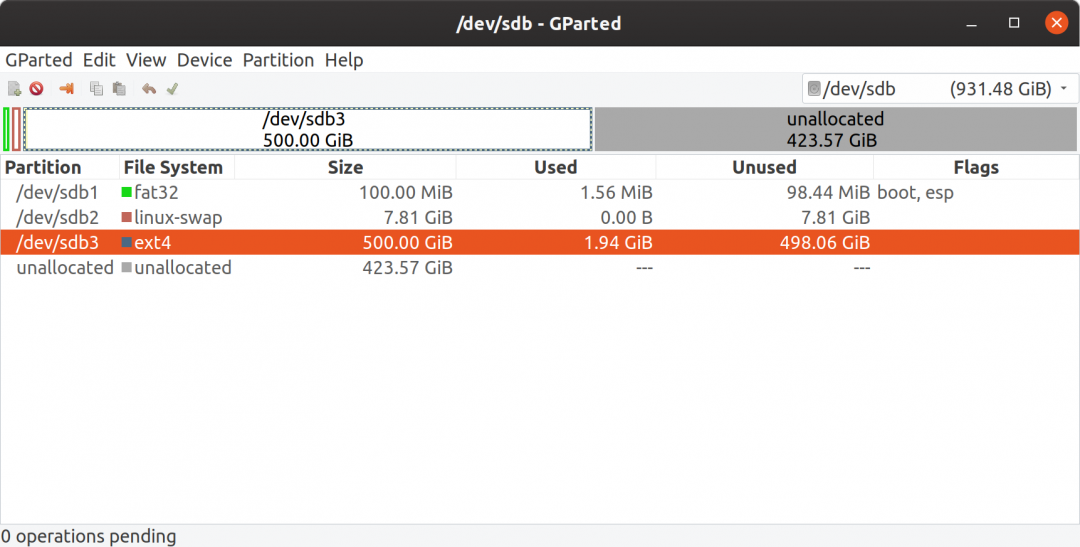
With the external drive all prepared, we now need to make a couple of notes, specifically - note the device and partition numbers. In this example my external drive is identified as /dev/sdb with partitions located on /dev/sdb1 (fat32 system/boot), /dev/sdb2 (linux-swap), /dev/sdb3 (ext4 root volume). We also need to record the UUIDs of the system and root volumes for this drive. Double click on the fat32 system partition at /dev/sdb1, and from the ‘Information about’ screen that pops up - make a note of the UUID. In my case: ED3C-7CB8. Now do the same for the root volume - the ext4 partition on /dev/sdb3 - double click on the partition and note the UUID. In my case: dd8eed75-c315-420f-b208-92301cfbf300.
We’re now almost ready to install Ubuntu 19.10 on this drive. Note first however, that in two attempts at this process, the system volume of the computer I was using for this process (my Windows 10 computer) was modified and left with a dual boot installation, which is NOT what we want (as that would effectively ‘bind’ our external hard drive to this computer). When we install Ubuntu 19.10 - we’ll mainly follow the instructions here - How to install Ubuntu on portable external Hard Drive? - however, during installation - Ubuntu 19.10 will use the first UEFI system partition it finds to install the modified bootloader, and so the instructions in the previous link that specify the following: “Very important: change the installation of the bootloader to the USB HD. This will most likely be /dev/sdb. This will prevent you from overwriting the master boot record on your hard drive. (If you do this by accident, it's easily fixed).” - simply won’t work. The only scenario I’ve not yet tried to prevent this is unplugging, or removing the computer’s internal hard drive before installing Ubuntu onto our target external drive. The remaining steps will show how to fix this, as well as how to correctly install a working GRUB bootloader onto our newly created /dev/sdb1 system fat32 ESP partition.
D. Install Ubuntu 19.10
With your external target drive all prepared we’re now ready to install Ubuntu 19.10. As per the link in the previous section, we’re going to start a normal installation followed by ‘Something else’ when we get to the partition selection step. You should still be booted from your Ubuntu Installation media thumb drive.
Close GParted and then double click on the Install Ubuntu 19.10 icon on your desktop. Choose your language settings, and optionally install third-party drivers. On the next screen, for ‘Installation Type’ - choose the last option ‘Something else’ before proceeding.
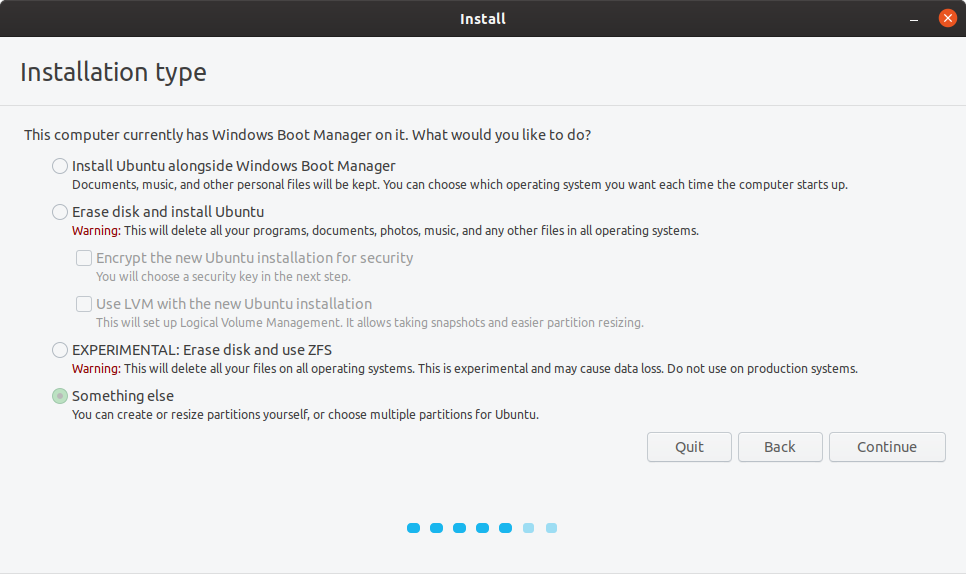
Now that we’re on the ‘Something else’ installation type screen - scroll down the list of available drive volumes until you see your device and the partitions we previously created. In this example /dev/sdb1, /dev/sdb2, and /dev/sdb3.
- Double click on the 100MB fat32 system efi partition we created (/dev/sdb1)and choose ‘Use as EFI system partition’ but do not format the partition.
- Double click on the /dev/sdb2 partition and choose ‘Use as swap area’.
- Then double click on the /dev/sdb3 partition - and choose use as 'Ext4 journaling file system’, and set the mount point to / or root, and again do not format this partition.
- Lastly - select the ‘Device for boot loader installations:’ to the name of the device for your external hard drive (although as noted above, this may not work and you’ll need to follow the remaining steps below).
Your settings should look like the following:
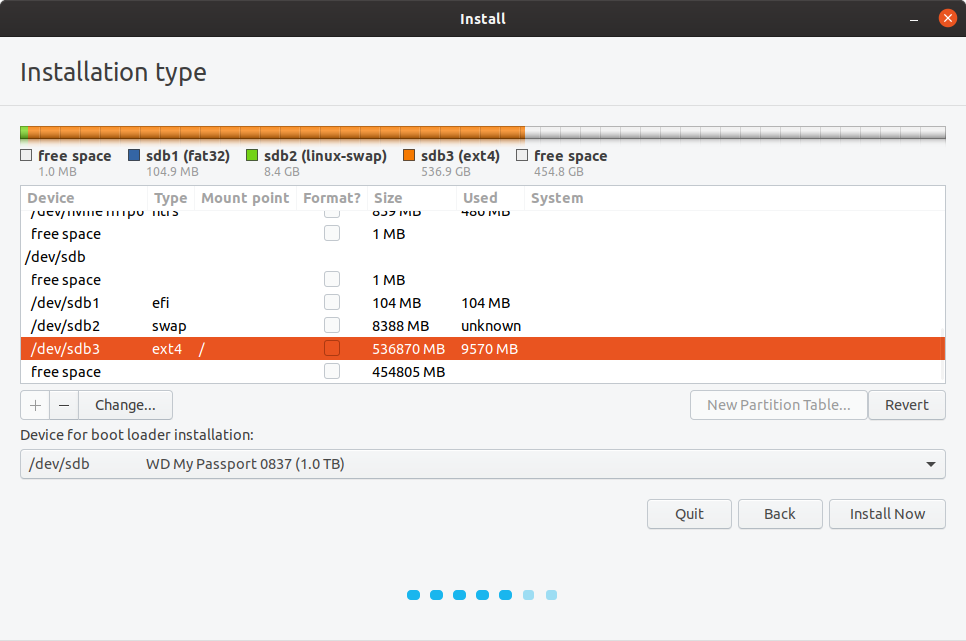
Go ahead now and install Ubuntu 19.10 to your external drive - setting your timezone, and user account information as you would with a normal Ubuntu installation.
E. Install Grub onto the ESP partition
As previously mentioned, the Ubuntu 19.10 installation process will likely have created a ‘dual boot’ installation by modifying your host computer's main EFI / ESP partition, effectively ‘binding’ your external drive to this computer. If so, there are two remaining tasks.
First, we need to correctly install the Grub bootloader onto the boot partition of our external portable drive - turning it into a truly portable installation.
The second and last step will be to remove the ‘dual boot’ configuration from the computer you are using to create this new external and portable drive. You can check to see if any of this applies to you by rebooting your computer WITH the new external drive plugged in - but selecting your computers primary disk (not the external disk) to boot from. If you see a ‘dual boot’ Grub option screen - then everything that follows applies.
Make sure you’re now booted from the Ubuntu installation thumb drive (in the ‘Try Ubuntu mode), and start the ‘Terminal’ application.
First we’re going to unmount the media volume of the thumb drive (leaving ‘Try Now’ Ubuntu running in memory only). Replace the 'uuid of your media' text below with the uuid in your system. There should be only one under media/ubuntu.
sudo umount /media/ubuntu/<the uuid of your media>
Now we’ll mount our new Ubuntu installation root volume from our external drive..
sudo mount /dev/sdb3 /mnt
We now need to fixup the UUIDs of the mount points in fstab for our external Ubuntu installation using the UUIDs we made a note of earlier:
sudo nano /mnt/etc/fstab
Copy and then comment the line with the /boot/efi mount point. In your new line replace the current UUID with the one from above - in this case ED3C-7CB8
The swap and root /mount points should be pointed to the correct volumes on our external drive. Save and close the file
Now we need to mount our new EFI / ESP system partition - our 100MB fat32 partition on /dev/sdb1
sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/efi
We now need to create some special system process mount points in our ‘simulated’ Ubuntu system, so that we can chroot into this volume and install Grub from the Ubuntu installation of our external drive itself (it must be installed using the same OS as the loader will target at boot).
sudo mount -B /dev /mnt/dev
sudo mount -B /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts
sudo mount -B /proc /mnt/proc
sudo mount -B /sys /mnt/sys
Next we’ll copy over our current DNS settings just in case we need network access...
sudo cp /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc/
Next we load efivars. The modprobe efivars command loads the efivars kernel module, which gives the kernel access to EFI variables stored in NVRAM
modprobe efivars
Finally we’ll switch into a chroot environment in our simulated OS on the external hard drive…
sudo chroot /mnt
And now after all that, we're ready to install Grub. As with all of the instructions above, be sure to change /dev/sdb with your own external drive device identifier.
grub-install -d /usr/lib/grub/x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot/efi/ --removable /dev/sdb
As Nicholas Dionysopoulos says in his excellent post "When you have an external drive it is critical that you use the –removable option in the last step. This installs the EFI bootloader under the special “fallback path” EFI\Boot\bootx64.efi in the ESP. Normally this not supposed to be used for permanently installed Operating Systems. It’s the mechanism used by EFI BIOS to boot arbitrary external media. Technically, that’s exactly what our external hard drive is: arbitrary external media"
Your new external drive should now be bootable in any machine.
F - Clean up the Dual Boot configuration
We now need to clean up the EFI / ESP partition on the computer you used to create the portable external drive. In order to boot this machine you’ll need to leave your new bootable external drive plugged in, or Grub will report an error and you won’t have any boot options. Reboot and choose your Windows installation to boot.
I now have a confession to make. I must have tried four or five different methods for removing the Grub dual boot configuration from my Windows 10 machine, including creating a full recovery media thumb drive and booting from it in recovery mode and attempting several commands I'd seen documented elsewhere. If anyone knows of the correct way to do this, please leave a comment below!
What worked in the end was the following:
Boot Windows and start a cmd window with administrator privileges:
Start the ‘DiskPart’ disk partition utility and list disks
list disk
Choose the hard disk that is your primary boot hard drive for this computer. Likely disk 0
select disk 0
Show the partitions on this disk
list partition
Select the EFI / ESP system partition (likely also 100MB)
select partition 1
Assign a free drive letter to this partition
assign letter=Z:
Exit DiskPart and change to the Z: drive Change into the EFI directory and remove the ubuntu sub-directory using:
rmdir /S ubuntu
Reboot your computer again, and your Windows installation should 'just start' as before - without any prompts from Grub or any sign of 'dual boot'.
After that - happy booting anywhere you like with your new external and portable hard drive.

Comments
Sorry but can you specify…
Sorry but can you specify this. When do i have to hit the e button? Between „try ubuntu“ and when ubuntu loads? Because this doesn‘t work for me.. I‘m very lost right now, is there an alternative solution?
Hi, I had the same problem…
Hi,
I had the same problem. Easy solution: I started again GParted and unmounted from there.
This is an amazing tutorial. Thank you so much for putting this together. It's (almost) a dream come true.
Regards,
Stéphan
Hey man! Thanks for the…
Hey man! Thanks for the guide.
I'm having some major problems in section E an I'm hoping you could help me out. After typing in the command sudo nano /mnt/etc/fstab, it becomes completely unclear what to do.
I'm a first time Linux user and I'm completely stuck here. Any help would be appreciated, thanks.
I’m having the same issue!
I’m having the same issue!
Hello Anthony, I want to say…
Hello Anthony, I want to say two things:
1. Many thanks for the clear instructions. I now have an external, bootable, portable USB Ubuntu installation (which has become important for my work during this crisis), and it's working perfectly. Actually, before seeing your article I saw that post by Nicholas Dionysopoulos which you praised. I tried to work through it but it was difficult for me to follow, and so I ended up at first trying the "easier" sets of instructions that I found. None worked for the reasons you mentioned. So I was very thankful in the end to find your instructions, which I found easier to follow than those of Nicholas. It was also very helpful that you identified and explained where the easier methods failed. So my first point is just to say thanks.
2. The second point is to share how I solved, or rather avoided, the problem that you describe in your section 'F'. One difference I should mention is that I wasn't using a Windows 10 machine to do this, but a machine running Xubuntu 16.04. In any case, just as you described, the setup process stepped on my machine's boot configuration and I would have no idea how to recover it. The way I solved it was that, anticipating problems, I first backed up the entire raw contents of the disk, including boot configuration and partitions, using Clonezilla. Then, after setting up the bootable USB drive, I restored from my Clonezilla backup and the machine was back to normal. As I mentioned I didn't try this with a Windows 10 machine, but my understanding is that Clonezilla works on Windows machines as well, so I'm guessing the results would be the same but I can't vouch for it. Anyway Clonezilla works perfectly on my Xubuntu computers, I have had to restore to various machines several times and always without problem.
All best,
Jonathan
Thanks very much for the…
Thanks very much for the comments Jonathan. And yes - creating a 'disposable' host to run through the process is a great idea. I've seen a couple of other posts that suggest just unplugging your main OS drive, and installing directly to your target portable drive, but I don't believe that will solve the need to install grub with the --removable option (which is why you have to jump through all of these hoops in the first place).
I had wrote over my windows…
I had wrote over my windows boot record a while back and was bypassing windows completely and only use kubuntu. Now I can't boot without using this external I can't wait to use later :) Have you ran into this before? I can't seem to be able to repair, restore or re-install using the Windows 10 iso. It's not picking up my driver's for some reason. I know I have a perfectly good file system and even recovery set up that aren't visible when using the Windows iso. Thanks
Hi... Firstly thanx. I'm…
Hi... Firstly thanx. I'm trying to achieve the same desired final result and confident I will with these great instructions.
I just wanted to add a couple of tips for my fellow newbies :
(1) I use Ventoy utility to boot from my desired live distros for testing purposes and/or installation and it works just fine.
(2) I reccomend you have a copy of Boot-Repair-CD ISO ... http://sourceforge.net/p/boot-repair-cd/home ... essential should you inadvertedly cripple your dual-boot pc like I did !
I believe you may also find this tool in ZorinOS and Partedmagic ISOs.
Hope this tip may help some in case of need.
Hello! Thank you for the…
Hello!
Thank you for the detailed walkthrough. I am trying to get ubuntu 18.04 working on my external drive. I followed the instructions, but with an 18.04 installation. The drive is now being detected by my system, but when I try to boot it it does not seem to detect the OS partition, I get the following error when I try to boot from the device: "error: file '\boot\' not found". Do you have any clue why this issue occurs? Any help is appreciated.
Thanks
Hey, got the same problem…
Hey, got the same problem here.
Have you manage to fix this issue ?
I got all the way to the…
I got all the way to the very last command. It says "the system cannot find the file specified"
Does anyone know where I went wrong?
So I followed all the steps…
So I followed all the steps on my windows desktop and have so when I turn it on without my ubuntu drive plugged in it boots into windows directly and when it is plugged in it boots directly to it without me having to change anything, however, this did not work on my laptop, a Dell XPS, I can boot into my drive and loads everything fine but does not have the ease from my desktop, how would I go about troubleshooting this?
also within my boot menu, it recognizes the drive but not ubuntu itself IDK if that can help
I cannot understand why…
I cannot understand why Ubuntu does not make this a standard option, since with USB 3.0 it is the most sensible way to try out Linux.
Agreed!
Agreed!
I like to do the same with…
I like to do the same with Kali Linux and LUKS LVM combination, on all partitions. However, something went wrong. After I did all your steps, I and selected as boot drive the external h.d see "Welcome to GRUB! error:disk 'lvmid/....' not found. grub rescue> Maybe you can have a look on my 'extended' steps.
/dev/sdb1 XXX-1111 the EFI partition
root@kali:/home/kali# cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb3 old-disk
--- Logical volume ---
LV Path /dev/my-vg/root
LV Name root
VG Name my-vg
LV UUID 111111-1111-1111-1111-1111-1111-111111
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time my, 2020-07-18 11:57:57 +0000
LV Status available
# open 0
LV Size <11.18 GiB
Current LE 2861
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
- currently set to 256
Block device 254:1
root@kali:/home/kali# vgchange -a y my-vg
5 logical volume(s) in volume group "my-vg" now active
root@kali:/home/kali# mount /dev/my-vg/root /mnt
root@kali:/home/kali# cd /mnt/boot/
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mkdir efi
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/efi
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mount -B /dev/ /mnt/dev/
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mount -B /dev/pts/ /mnt/dev/pts
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mount -B /proc/ /mnt/proc/
root@kali:/mnt/boot# mount -B /sys/ /mnt/sys/
root@kali:/mnt/boot# modprobe efivars
root@kali:/mnt/boot# chroot /mnt/
root@kali:/# grub-install -d /usr/lib/grub/x86_64-efi/ --efi-directory=/boot/efi/ --removable /dev/sdb
Installing for x86_64-efi platform.
File descriptor 4 (/dev/sdb1) leaked on vgs invocation. Parent PID 2740: grub-install
File descriptor 4 (/dev/sdb1) leaked on vgs invocation. Parent PID 2740: grub-install
Installation finished. No error reported.
I am for some reason stuck…
I am for some reason stuck at part f. Where it says to change to z drive i changed to c but it won't go to z. do i need the complete path?
Hi Anthony, I'm having the…
Hi Anthony, I'm having the exact same problem as Emma
''Hi,
I stuck on part E:
sudo umount /media/ubuntu/the uuid of your media
I booted from USB and in Try Ubuntu mode, then run above command but it not worked (of course I already replace the uuid part with my USB partition uuid). My path is different. In /media/cdrom, there are folders and files like this:
autorun.ico dists md5sum.txt README.diskdefines
autorun.inf EFI pics syslinux.cfg
boot install pool 'System Volume Information'
casper isolinux preseed ubuntu
I tried 'sudo umount /media/cdrom/the uuid of your media' and it said 'no mount point specified'.
I tried 'sudo umount /dev/sdc1' (which is the only partition of USB), and it said 'umount: /cdrom: target is busy'.
I'm quite new to ubuntu. Please help me fix this. Thank you.''
Hoping you could provide some insight please.
I have completed step D with…
I have completed step D with a ubuntu 20 installation. Now it asks me to restart by removing the installation medium.
Now my first question is how to boot up with the thumb drive. Isn't it the same as using USB to load and using try ubuntu mode.
Now I am in the try ubuntu mode
But there is no ubuntu in the medium folder, it contains cdrom.
What to do?
Great guide! Here's one…
Great guide! Here's one suggestion.
You don't need to unplug the old hard drive. Instead, you can remove the drive from Ubuntu.
After booting to the "Ubuntu Installation media thumb drive", open a terminal and as root, type:
echo 1 > /sys/block/sdX/device/delete
Then run the installer, and grub never sees the original OS disk, so it can't update it.
See StackOverflow: (can't post the link here for some reason, but search for "Ubuntu How do I permanently disable hard drives")
Hi Ryan, Thanks very much…
Hi Ryan,
Thanks very much for the reply. Does this mean that the manual installation of Grub with the 'removable' option is no longer required?
Could you try again to submit the link?
I tried with Ryans input,…
I tried with Ryans input, did "D. Install Ubuntu 19.10" and skipped "E. Install Grub onto the ESP partition"
Seems to work fine for me on a late 2013 Macbook Pro. When USB is connected, it automatically boots into the drive. When disconnected it boots into OSX.
No need to run the "portable" command it seems? Not sure what that would give me.
However I have only tried it against this machine. Maybe will fail if connected to other machine?
Hi Anthony, It seems like…
Hi Anthony,
It seems like the --removable options is still good to have. (Didn't test that myself though)
Thanks Ryan - I'll check to…
Thanks Ryan - I'll check to see why you couldn't post the link on how to disable the host drive. Here it is in case anyone else is interested...
https://askubuntu.com/questions/554398/how-do-i-permanently-disable-har…
The first step in Part E…
The first step in Part E says:
First we’re going to unmount the media volume of the thumb drive (leaving ‘Try Now’ Ubuntu running in memory only). Replace the 'uuid of your media' text below with the uuid in your system. There should be only one under media/ubuntu.
sudo umount /media/ubuntu/I'm doing this from a live-debian thumb drive. Any idea what I should put here?
When I look at the live-debian thumb drive in Disks, it shows the first partition with the UUID of 2020-05-09-13-13-27-00, and it says it is mounted at /run/live/medium.
I'm thinking I should type
sudo unmount /run/live/medium/2020-05--9-13-13-27-00Any thoughts?
This was a very useful…
This was a very useful tutorial, and I was able to get it to work on a Windows 10 laptop on the main drive, with Ubuntu 20.04 installed to an NVMe drive inside a portable USB enclosure.
Question: If the linux kernel gets upgraded to a newer version (e.g. sudo apt-get dist-upgrade), does grub automatically run to due to the kernel upgrade? If so, will that re-bind the laptop to the portable Ubuntu drive again?